When ₦1,000 today buys less tomorrow, even though it might sometimes feel like overexpenditure, the culprit is inflation. This is a fictitious demonstration of how a bank account in Nigeria deals with inflation.
Savings account interest can add to the growth of a bank account by a small percentage. However, money in the bank can be impacted by an increasing inflation rate. Prices of goods that cost ₦200 last year could cost up to ₦240, assuming there was an inflation rise of 20%.
With a total balance of ₦208 in the bank, giving an interest rate of 4% added to a bank account of ₦200, it might be impossible to afford the same basket of goods if the price rises to ₦240, impacted by inflation.
- CNG, Electric Vehicles to Transform Transportation in Nigeria as FG Intensifies Push

- New Decision for Maryam Sanda as She Gets 12 Years

- China-Nigeria Sign $400m Deal to Boost Steel Production

The real value of a bank account with ₦208/year at a 4% annual interest is approximately ₦0.87, having seen a small growth in their monthly deposit to ₦240. With ₦1, they can now afford only 87 kobo worth of goods compared to the year before.
This model can be summarized in one phrase, “A bank account balance number goes up (thanks to interest), but purchasing power goes down (because inflation is much higher). This gap widens over a few years, at the current rate of inflation in Nigeria.
Inflation eats away at the real value of a naira bank account, even if the numbers go up. In a naira savings account, inflation erodes purchasing power because interest (4–6%) can not keep up with inflation rates.
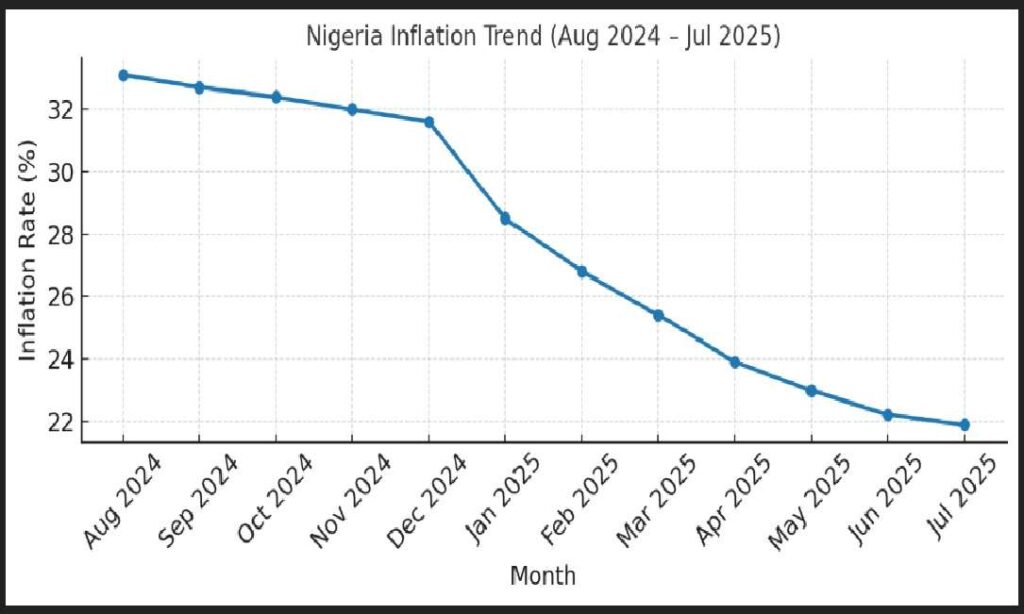
Inflation Snapshot for Nigeria — July 2025
Current rate July 2025: 21.88% year-on-year, down from 22.22% in June—marking four consecutive monthly declines.
Recent Trend:
- June 2025: Inflation was 22.22%, easing from 22.97% in May.
- The downward shift has been gradual since January’s sharp drop following a methodological rebasing of the index.
Inflation Compared to Previous Year
- 2024 Estimated Average Inflation: Around 31.4%.
- The current 21.88% rate in July 2025 suggests a significant moderation compared to early 2024 levels, where inflation was in the 30-plus percent range.
- More precisely, the July 2025 figure is roughly 9–10 percentage points lower than the average in 2024.
Here’s the year-on-year change:
- July 2025 headline inflation: 21.88%.
- July 2024 headline inflation: 33.40%.
Difference (YoY):
- −11.52 percentage points (33.40% − 21.88%).
- That’s approximately a 34.6% reduction relative to July 2024.







